In the intricate tapestry of nature, the biotic and abiotic venn diagram emerges as a captivating tool to unveil the dynamic relationship between living organisms and their non-living surroundings. This diagram provides a visual representation of the interplay between these two fundamental components, offering insights into the delicate balance that sustains our ecosystems.
The biotic realm encompasses all living organisms, from towering trees to microscopic bacteria, while the abiotic realm encompasses the physical and chemical factors that shape their existence. These factors include temperature, water availability, sunlight, and soil composition. By examining the overlapping area of the Venn diagram, we gain a deeper understanding of how these two realms interact, influencing the survival, distribution, and behavior of species.
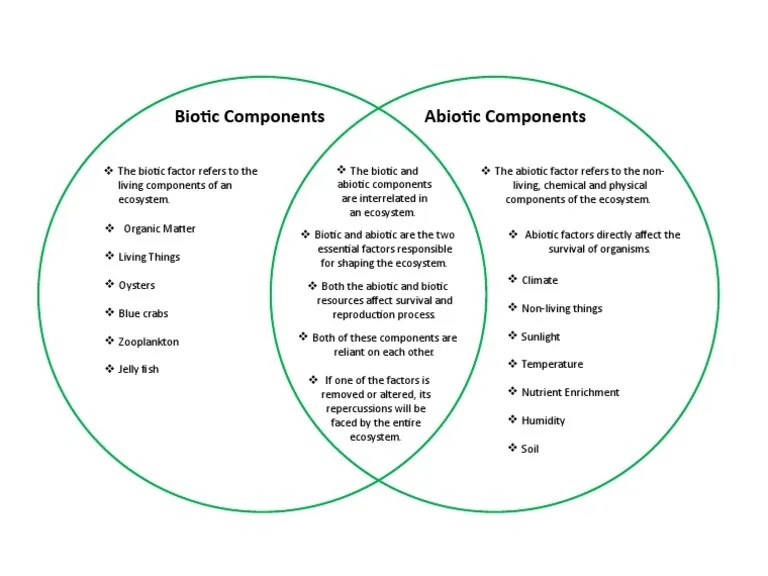
Biotic and Abiotic Components
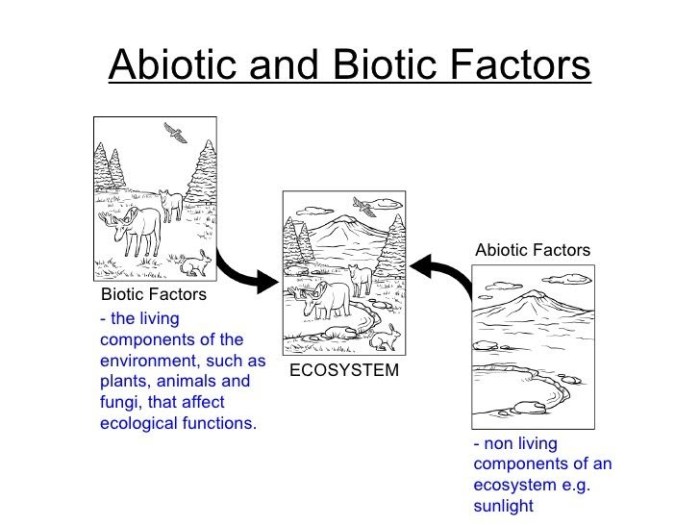
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms and their physical environment. The living organisms in an ecosystem are called biotic components, while the non-living physical environment is called abiotic components.
Biotic components include all living things, such as plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria. Abiotic components include the non-living physical factors that affect living organisms, such as sunlight, temperature, water, and soil.
Interdependence of Biotic and Abiotic Components
Biotic and abiotic components are interdependent. Living organisms depend on the non-living physical environment for their survival, and the non-living physical environment is affected by the activities of living organisms.
- For example, plants need sunlight, water, and nutrients from the soil to grow. In turn, plants provide food and shelter for animals.
- Animals breathe oxygen from the air and drink water from rivers and lakes. In turn, animals produce carbon dioxide and waste products that affect the composition of the atmosphere and water.
Venn Diagram Representation
A Venn diagram is a graphical representation that illustrates the relationship between two or more sets of data. It is commonly used to compare and contrast the similarities and differences between different groups or categories. In the context of biotic and abiotic components, a Venn diagram can effectively showcase the interactions and overlaps between these two fundamental elements of an ecosystem.
Overlapping Area
The overlapping area in a Venn diagram represents the shared characteristics or components between the two sets being compared. In the case of biotic and abiotic components, the overlapping area highlights the interactions and dependencies that exist between living organisms and their non-living surroundings.
This zone encompasses factors such as the influence of abiotic factors on the survival and distribution of organisms, as well as the impact of biotic components on shaping the abiotic environment.
Interactions between Biotic and Abiotic Factors
The Venn diagram serves as a valuable tool for visualizing the intricate interplay between biotic and abiotic factors within an ecosystem. It allows us to comprehend how abiotic components, such as temperature, water availability, and soil composition, can influence the distribution, growth, and behavior of organisms.
Conversely, the diagram also demonstrates how biotic components, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, can modify their abiotic surroundings through processes like nutrient cycling, soil formation, and climate regulation. By illustrating these interactions, the Venn diagram underscores the interconnectedness and interdependence of all components within an ecosystem.
Specific Ecosystems
Ecosystems, whether forests, grasslands, or aquatic environments, are complex and dynamic systems where living organisms (biotic components) interact with their physical and chemical surroundings (abiotic components). These interactions shape the characteristics and functioning of the ecosystem.
The biotic components of an ecosystem include plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms, while the abiotic components encompass factors like temperature, precipitation, soil type, and sunlight. Understanding the interplay between these components is crucial for comprehending the intricate balance that sustains ecosystems.
Forest Ecosystem
Forests, characterized by dense vegetation, are home to a diverse array of biotic components, including trees, shrubs, herbs, animals, insects, and microorganisms. The abiotic components of a forest include sunlight, temperature, humidity, soil type, and water availability.
The interaction between biotic and abiotic factors in a forest ecosystem is evident in the following ways:
- Trees absorb sunlight for photosynthesis, which provides energy for the ecosystem.
- The canopy formed by trees regulates temperature and humidity, creating a microclimate.
- Soil type and water availability influence the distribution of plant species and their growth.
- Animals rely on plants for food and shelter, while plants provide oxygen and habitat for animals.
- Microorganisms decompose organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the soil.
Grassland Ecosystem, Biotic and abiotic venn diagram
Grasslands are characterized by vast expanses of grasses and other herbaceous plants. The biotic components of a grassland ecosystem include grazing animals, insects, birds, and microorganisms. The abiotic components include sunlight, temperature, precipitation, and soil type.
Biotic and abiotic components form a crucial part of our ecosystem. Just like the iconic first name in Gattaca posters , they play a significant role in shaping our environment. By understanding their interactions, we gain insights into the delicate balance of nature, making the study of biotic and abiotic venn diagrams essential for comprehending the world around us.
The interactions between biotic and abiotic factors in a grassland ecosystem are as follows:
- Grasses convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, providing sustenance for the ecosystem.
- Grazing animals regulate the growth and distribution of grasses.
- Insects and birds pollinate plants and control insect populations.
- Microorganisms decompose organic matter, enriching the soil.
- Temperature and precipitation patterns influence the productivity and species composition of grasslands.
Aquatic Ecosystem
Aquatic ecosystems, encompassing oceans, lakes, rivers, and wetlands, support a diverse array of biotic components, including fish, aquatic plants, invertebrates, and microorganisms. The abiotic components of an aquatic ecosystem include water temperature, salinity, pH, dissolved oxygen, and water depth.
The interactions between biotic and abiotic factors in an aquatic ecosystem are as follows:
- Aquatic plants produce oxygen through photosynthesis, supporting the respiration of other organisms.
- Water temperature influences the metabolic rates and distribution of aquatic organisms.
- Salinity affects the survival and distribution of organisms adapted to different salt concentrations.
- Dissolved oxygen levels are crucial for the survival of aquatic organisms that rely on oxygen for respiration.
- Water depth influences the availability of sunlight and the distribution of aquatic organisms.
Environmental Impact: Biotic And Abiotic Venn Diagram
Human activities can significantly impact the balance between biotic and abiotic components in an ecosystem. These activities can disrupt the delicate interactions between living organisms and their environment, leading to a range of environmental issues.
One of the most significant ways human activities affect ecosystems is through pollution. Pollution can come in various forms, such as air pollution, water pollution, and soil pollution. Pollutants can harm both biotic and abiotic components of an ecosystem, disrupting their interactions and affecting the overall health of the ecosystem.
Disruption of Biotic and Abiotic Interactions
- Pollution can harm living organisms directly, affecting their growth, reproduction, and survival.
- Pollution can also alter the physical and chemical properties of the environment, making it less suitable for certain species.
- For example, acid rain can damage forests and aquatic ecosystems, while oil spills can harm marine life.
Strategies for Mitigating Negative Effects
- Reducing pollution is crucial for mitigating the negative effects of human activities on ecosystems.
- This can be achieved through measures such as promoting renewable energy, improving waste management, and implementing stricter environmental regulations.
- Additionally, conservation efforts, such as protecting and restoring habitats, can help maintain the balance between biotic and abiotic components in ecosystems.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the significance of the overlapping area in the biotic and abiotic venn diagram?
The overlapping area represents the zone of interaction between living organisms and their non-living environment. It highlights the factors that influence the survival, distribution, and behavior of species.
How can human activities disrupt the balance between biotic and abiotic components?
Human activities such as pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change can alter the physical and chemical conditions of the environment, impacting the survival and distribution of species.
