What is a chelating agent milady – Embark on a fascinating journey into the world of chelating agents, milady! These remarkable substances possess an extraordinary ability to embrace metal ions in a captivating dance of molecular attraction. Delve into their enchanting properties, unravel their diverse applications, and discover the secrets of their ingenious design.
Chelating agents, like graceful ballerinas, gracefully wrap themselves around metal ions, forming intricate complexes that waltz through a myriad of industrial and medical processes. Their elegance extends beyond their aesthetic charm, as they play pivotal roles in water purification, metal finishing, and the intricate realm of medicine.
Chelating Agent Overview: What Is A Chelating Agent Milady
A chelating agent is a chemical compound that can form multiple bonds to a metal ion. Chelating agents are often used to remove metal ions from solution or to prevent them from reacting with other compounds.
Chelating agents work by surrounding the metal ion with multiple atoms or groups of atoms, which form strong bonds with the metal ion. This prevents the metal ion from interacting with other compounds or from precipitating out of solution.
Examples of Common Chelating Agents
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA)
- Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA)
- Nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA)
Chelating Agent Properties
Chelating agents possess distinct properties that contribute to their versatility in various applications. These agents are characterized by their ability to form stable complexes with metal ions, known as chelates. This complexation process involves the coordination of multiple donor atoms from the chelating agent to the metal ion, resulting in the formation of a ring-like structure.
The strength of the chelate complex is influenced by several factors, including the number and type of donor atoms, the size and charge of the metal ion, and the pH of the solution. Chelating agents with a higher number of donor atoms tend to form stronger complexes.
Additionally, the size and charge of the metal ion affect the stability of the complex, with smaller and higher-charged metal ions forming more stable chelates.
Key Properties of Chelating Agents
- Multidentate:Chelating agents have multiple donor atoms that can coordinate with metal ions, forming stable complexes.
- High Affinity:Chelating agents exhibit a high affinity for metal ions, forming strong and stable complexes.
- Selectivity:Chelating agents can exhibit selectivity for specific metal ions, allowing for the selective removal or complexation of desired metals.
- Water Solubility:Many chelating agents are water-soluble, enabling their use in aqueous solutions.
- Biocompatibility:Some chelating agents are biocompatible and can be used in biological systems for various applications, such as metal ion detoxification and drug delivery.
Role of Chelation in Various Applications
Chelating agents play crucial roles in numerous applications across various industries and disciplines. Some of the key applications include:
- Water Treatment:Chelating agents are used to remove heavy metal ions from water sources, preventing their accumulation and potential toxicity.
- Metal Ion Analysis:Chelating agents are employed in analytical chemistry to determine the concentration of metal ions in various samples.
- Metal Extraction:Chelating agents are used in the mining industry to extract and recover valuable metals from ores.
- Pharmaceuticals:Chelating agents are used as therapeutic agents to remove toxic metals from the body in cases of metal poisoning or overdose.
- Textile Industry:Chelating agents are used in the textile industry to improve the dyeing process and prevent metal ion discoloration.
Chelating Agent Applications
Chelating agents find diverse applications in various industries due to their ability to bind metal ions and form stable complexes. Their unique properties make them valuable in water treatment, metal finishing, and medicine, among other areas.
In water treatment, chelating agents are employed to remove heavy metal ions from water sources. They prevent these metals from forming scale or deposits in pipes and equipment, ensuring the quality and safety of drinking water.
Metal Finishing, What is a chelating agent milady
In metal finishing, chelating agents play a crucial role in various processes, including electroplating, metal cleaning, and polishing. They help control the deposition of metal ions onto surfaces, resulting in smoother and more uniform coatings. Chelating agents also assist in removing impurities and contaminants from metal surfaces, improving the adhesion and durability of coatings.
Medicine
In medicine, chelating agents are used to treat heavy metal poisoning, such as lead and mercury toxicity. They bind to the metal ions and facilitate their excretion from the body, reducing their harmful effects. Chelating agents also find application in diagnostic imaging, where they enhance the visibility of specific organs or tissues by forming complexes with metal-based contrast agents.
Chelating Agent Mechanism
Chelating agents function by binding to metal ions through their multiple coordinating atoms, forming stable complexes. This process involves the donation of electron pairs from the chelating agent to the metal ion, creating coordinate bonds.
Complex Formation
The chelating agent’s coordinating atoms, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur, have lone pairs of electrons that can be shared with the metal ion. These atoms form coordinate bonds with the metal ion, resulting in the formation of a complex.
The number and arrangement of coordinating atoms determine the stability and geometry of the complex.
The stability of the complex is influenced by factors such as the size and charge of the metal ion, the number and type of coordinating atoms, and the electronegativity of the chelating agent.
Chelating Agent Design
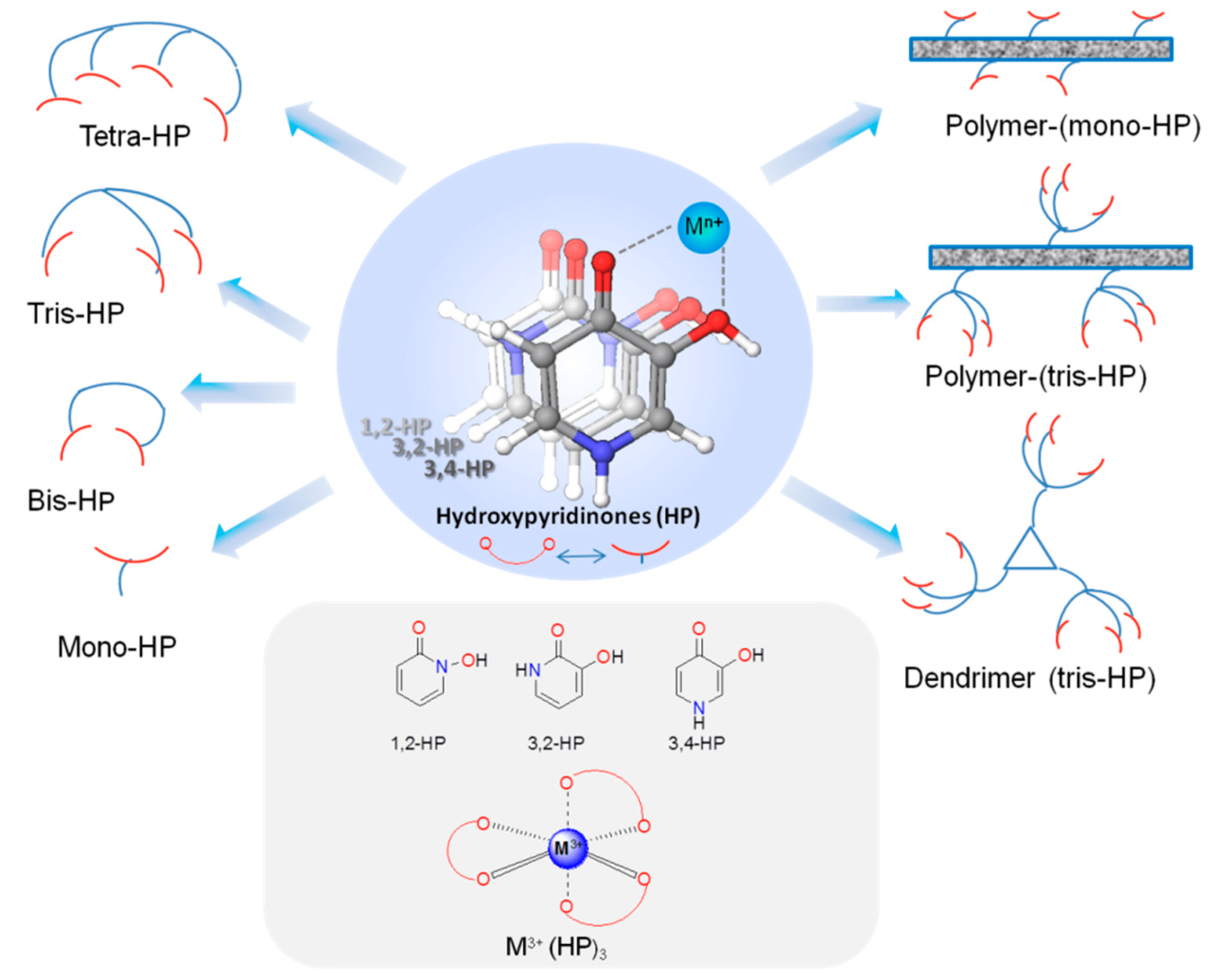
Chelating agent design is a complex process that requires careful consideration of several factors, including the target metal ion, the desired stability of the chelate complex, and the potential toxicity of the chelating agent. The design of chelating agents is guided by several principles, including:
- Chelate effect:The chelate effect refers to the increased stability of a metal complex formed by a chelating agent compared to a complex formed by a monodentate ligand. The chelate effect is due to the formation of multiple bonds between the metal ion and the chelating agent, which results in a decrease in the entropy of the system.
- Ring size:The size of the chelate ring is also an important factor in determining the stability of the complex. Smaller rings are generally more stable than larger rings, as they result in less strain on the metal ion.
- Functional groups:The functional groups present on the chelating agent can also affect the stability of the complex. Chelating agents with electronegative functional groups, such as oxygen or nitrogen, are generally more stable than those with less electronegative functional groups, such as carbon or hydrogen.
Chelating agents are typically synthesized by reacting a metal ion with a ligand that contains multiple donor atoms. The reaction conditions, such as the temperature and pH, can affect the yield and purity of the chelating agent. The chelating agent can then be optimized by modifying the functional groups or the ring size to improve its stability or selectivity for a particular metal ion.
Successful Chelating Agent Designs
There are many examples of successful chelating agent designs. One of the most well-known chelating agents is EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid). EDTA is a hexadentate chelating agent that forms stable complexes with a wide variety of metal ions. EDTA is used in a variety of applications, including water softening, metal finishing, and analytical chemistry.
Another example of a successful chelating agent design is DOTA (1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid). DOTA is an octadentate chelating agent that forms very stable complexes with lanthanide ions. DOTA is used in a variety of applications, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and nuclear medicine.
General Inquiries
What is the primary purpose of a chelating agent?
Chelating agents are designed to bind to metal ions, forming stable complexes that prevent them from reacting with other substances.
Can chelating agents be used in everyday life?
Yes, chelating agents find applications in various household products, such as detergents and water softeners, where they help remove metal ions that can cause stains or scale buildup.
Are chelating agents harmful to humans?
Some chelating agents can be toxic if ingested in large quantities, but those used in commercial products are generally safe when used as directed.