Foreign vs domestic policy worksheet answers provide a structured framework for understanding the key differences between foreign and domestic policies, their implementation, and their impact. This comprehensive guide explores these concepts, offering insights into the decision-making processes, international organizations’ roles, and the analysis of policy effectiveness.
Delving into the nuances of foreign and domestic policies, this guide equips readers with a thorough understanding of their respective scopes, types, and consequences for citizens.
Foreign Policy: Foreign Vs Domestic Policy Worksheet Answers
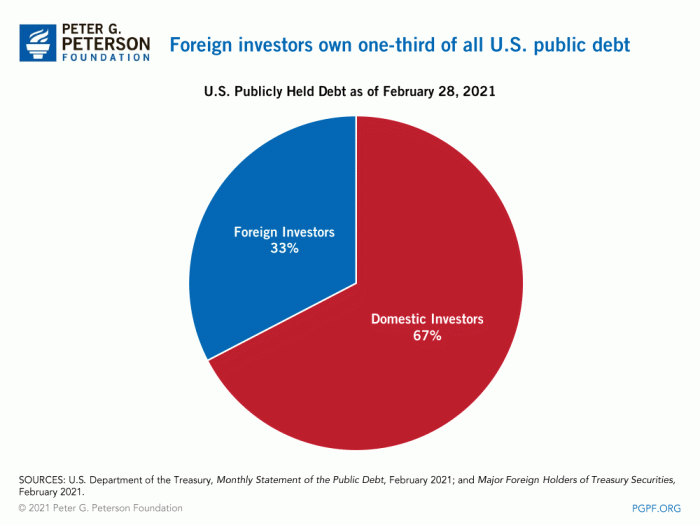
Foreign policy encompasses the decisions and actions taken by a government to interact with other countries and influence the global environment. It differs from domestic policy, which focuses on internal affairs within a country’s borders.
Key differences between foreign and domestic policy include:
- Scope:Foreign policy deals with international relations, while domestic policy addresses internal issues within a country.
- Actors:Foreign policy involves interactions between governments, international organizations, and non-state actors, while domestic policy primarily involves government interactions with its citizens.
- Objectives:Foreign policy aims to protect national interests, promote cooperation, and influence global events, while domestic policy focuses on improving the well-being of citizens.
Examples of foreign policy decisions include:
- Establishing diplomatic relations with other countries
- Negotiating trade agreements
- Participating in international organizations
- Providing foreign aid
- Using military force
International organizations play a significant role in foreign policy by facilitating cooperation, resolving conflicts, and promoting global governance.
Domestic Policy
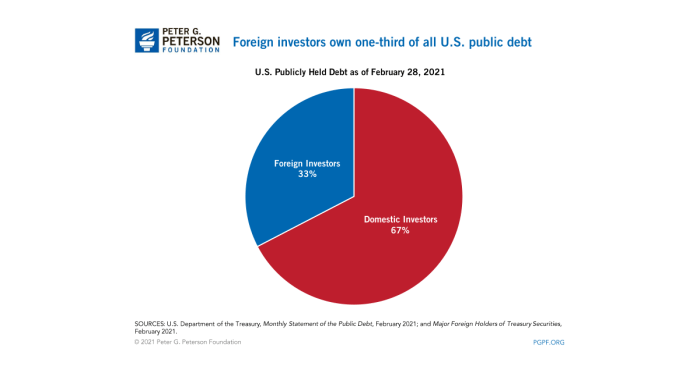
Domestic policy refers to the decisions and actions taken by a government to manage its internal affairs and address issues within its borders.
Scope of domestic policy includes:
- Economic policies (e.g., taxation, monetary policy, trade)
- Social policies (e.g., education, healthcare, welfare)
- Environmental policies (e.g., climate change, pollution control)
- Security policies (e.g., law enforcement, military, national security)
Different types of domestic policies implemented by governments include:
- Fiscal policy:Deals with government spending, taxation, and public debt.
- Monetary policy:Controls the money supply and interest rates.
- Social welfare policy:Provides support to citizens in need (e.g., unemployment benefits, healthcare, housing assistance).
- Education policy:Governs the provision and regulation of education.
- Environmental policy:Regulates activities that affect the environment.
Domestic policies have a significant impact on citizens’ lives, affecting their economic well-being, health, safety, and access to opportunities.
FAQs
What is the primary distinction between foreign and domestic policy?
Foreign policy focuses on a nation’s interactions with other countries and international organizations, while domestic policy deals with internal affairs within a country’s borders.
How do international organizations influence foreign policy?
International organizations provide platforms for dialogue, cooperation, and conflict resolution, shaping the interactions between nations and influencing foreign policy decisions.
What are the common types of domestic policies implemented by governments?
Domestic policies encompass a wide range, including economic policies (e.g., fiscal, monetary), social policies (e.g., healthcare, education), and environmental policies (e.g., climate change mitigation).
How is the effectiveness of different policy approaches evaluated?
Policy analysis involves assessing the outcomes, costs, and benefits of different policy options, considering factors such as intended and unintended consequences, efficiency, and equity.