A dolphin perceives its environment by the sense of echolocation, vision, hearing, touch, taste, and smell. This intricate sensory system allows them to navigate their complex underwater world, communicate effectively, and detect potential threats. Let’s delve into the remarkable sensory capabilities of these fascinating marine mammals.
Echolocation, a dolphin’s primary sense, enables them to create and interpret sound waves to form a detailed mental map of their surroundings. Their exceptional hearing allows them to detect a wide range of sounds, from prey to potential predators.
Dolphin Sensory Perception

Dolphins possess a remarkable array of sensory capabilities that enable them to navigate their aquatic environment with precision. Among their most notable senses are echolocation, vision, hearing, touch, taste, and smell.
Echolocation
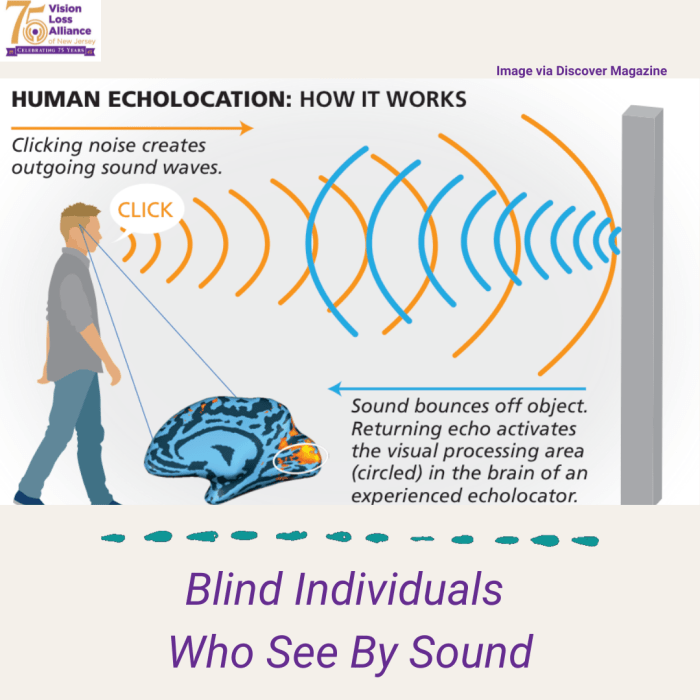
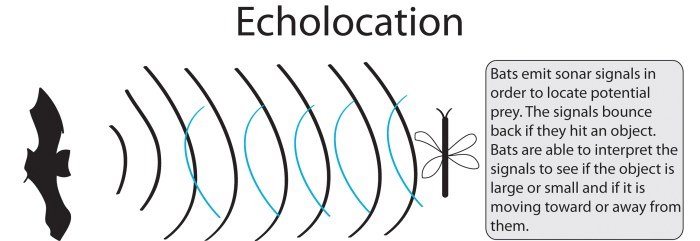
Echolocation is a sophisticated sonar system that dolphins use to perceive their surroundings. By emitting high-pitched clicks and listening for the returning echoes, dolphins can create a detailed mental map of their environment. This allows them to detect objects, determine their size and shape, and identify obstacles in their path.
Echolocation is particularly advantageous in murky or low-light conditions, where vision is limited. It also provides dolphins with a means of hunting prey and communicating with each other.
Advantages of Echolocation:
- Allows dolphins to navigate and hunt in low-visibility conditions.
- Provides detailed information about the size, shape, and location of objects.
- Enables dolphins to communicate with each other over long distances.
Limitations of Echolocation:
- Can be affected by background noise or interference from other sound sources.
- Provides limited information about the color or texture of objects.
- Requires dolphins to produce high-frequency clicks, which can be detected by predators.
Vision
Dolphins have excellent vision, both above and below the water’s surface. Their eyes are adapted to low-light conditions and can detect a wide range of colors. Dolphins use vision for navigation, predator detection, and social interactions.
In addition to binocular vision, dolphins also have monocular vision, allowing them to see in two different directions simultaneously. This provides them with a wider field of view and enhances their ability to scan their surroundings.
Hearing, A dolphin perceives its environment by the sense of
Dolphins have exceptional hearing capabilities. Their ears are located on the sides of their head and are sensitive to a wide range of frequencies. Dolphins use hearing for communication, navigation, and predator detection.
The range of dolphin hearing extends from low-frequency sounds to ultrasonic frequencies. This allows them to detect prey, communicate with each other over long distances, and avoid predators.
Touch
Dolphins have a highly developed sense of touch. Their skin is covered in sensitive nerve endings that allow them to perceive pressure, temperature, and texture. Dolphins use touch for social interactions, communication, and object manipulation.
Dolphins often rub against each other to establish social bonds and communicate. They also use their flippers to manipulate objects and explore their environment.
Taste and Smell
Dolphins have a limited sense of taste and smell. Their taste buds are located on the back of their tongue and are sensitive to sweet, salty, and bitter flavors. Dolphins use taste to evaluate the quality of food and may also play a role in social interactions.
Dolphins have a small olfactory bulb, indicating a limited sense of smell. They may use smell to detect chemical cues in the water and for communication purposes.
Sensory Integration
Dolphins rely on the integration of information from multiple senses to perceive their environment. Their brains are highly developed and capable of processing and interpreting sensory information from echolocation, vision, hearing, touch, taste, and smell.
Sensory integration allows dolphins to create a comprehensive and accurate representation of their surroundings. This enables them to navigate complex environments, locate prey, avoid predators, and engage in social interactions.
Clarifying Questions: A Dolphin Perceives Its Environment By The Sense Of
How do dolphins use echolocation?
Dolphins emit high-frequency sound waves and interpret the echoes to create a detailed mental map of their surroundings.
What are the advantages of echolocation for dolphins?
Echolocation allows dolphins to navigate in low-visibility conditions, hunt prey, and detect predators.
How do dolphins use vision?
Dolphins have excellent eyesight, both above and below water, which they use for communication, social interactions, and prey detection.