Bohr and Lewis dot diagrams worksheet answers provide a comprehensive understanding of atomic structure and chemical bonding. These diagrams are essential tools for students and professionals in chemistry, allowing them to visualize and analyze the electronic configurations of elements and molecules.
This guide offers a thorough explanation of Bohr and Lewis dot diagrams, including their definitions, purposes, and applications. It also includes a downloadable worksheet with practice exercises and answer key to enhance comprehension.
Bohr and Lewis Dot Diagrams
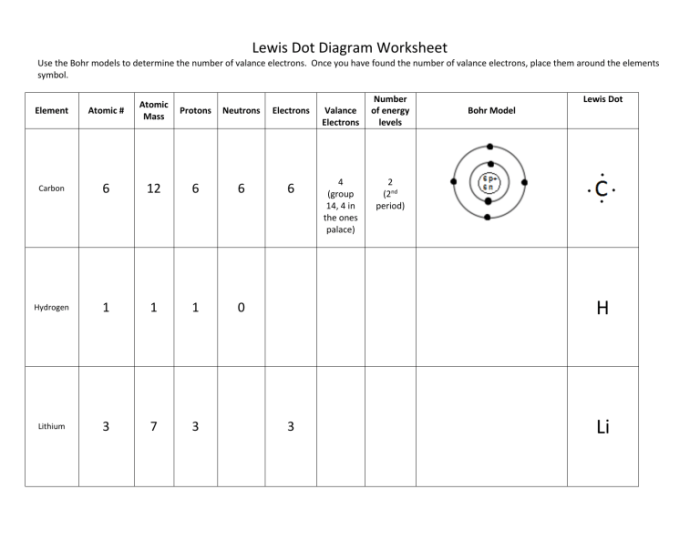
Bohr diagrams and Lewis dot diagrams are two important tools used by chemists to visualize the structure of atoms and molecules.
Bohr Diagrams, Bohr and lewis dot diagrams worksheet answers
Bohr diagrams, also known as atomic models, represent the arrangement of electrons in an atom. They were developed by Niels Bohr in 1913 and are based on the idea that electrons orbit the nucleus in discrete energy levels.
Each energy level is represented by a circle, and the electrons are represented by dots. The number of circles and the number of dots in each circle represent the number of energy levels and the number of electrons in each energy level, respectively.
For example, the Bohr diagram of hydrogen has one circle with one dot, representing the single electron in the first energy level.
Lewis Dot Diagrams
Lewis dot diagrams, also known as electron dot diagrams, represent the valence electrons in an atom or molecule. They were developed by G.N. Lewis in 1916 and are based on the idea that atoms can form chemical bonds by sharing electrons.
In a Lewis dot diagram, the element symbol is written in the center, and the valence electrons are represented by dots around the symbol. The number of dots represents the number of valence electrons.
For example, the Lewis dot diagram of hydrogen has one dot, representing the single valence electron.
Worksheet
A worksheet with practice exercises on Bohr and Lewis dot diagrams is available for download.
The worksheet includes a mix of multiple choice, short answer, and diagram-drawing questions.
An answer key is also provided.
Table of Elements
A table of elements with their corresponding Bohr and Lewis dot diagrams is available for download.
The table includes the element name, symbol, atomic number, Bohr diagram, and Lewis dot diagram.
Comparison of Bohr and Lewis Dot Diagrams
Bohr diagrams and Lewis dot diagrams are both useful tools for visualizing the structure of atoms and molecules.
However, there are some key differences between the two diagrams.
Bohr diagrams show the arrangement of all the electrons in an atom, while Lewis dot diagrams only show the valence electrons.
Bohr diagrams are more detailed than Lewis dot diagrams, but they can be more difficult to draw.
Lewis dot diagrams are simpler to draw and are more useful for predicting chemical bonding.
Applications of Bohr and Lewis Dot Diagrams
Bohr diagrams and Lewis dot diagrams are used in a variety of applications in chemistry.
Bohr diagrams are used to explain the properties of atoms, such as their ionization energy and electron affinity.
Lewis dot diagrams are used to predict the chemical bonding of atoms and molecules.
Both Bohr diagrams and Lewis dot diagrams are essential tools for understanding the structure and properties of atoms and molecules.
FAQ Corner: Bohr And Lewis Dot Diagrams Worksheet Answers
What is the difference between a Bohr diagram and a Lewis dot diagram?
Bohr diagrams depict the arrangement of electrons in an atom’s orbitals, while Lewis dot diagrams show the valence electrons involved in chemical bonding.
How can I use Bohr and Lewis dot diagrams to predict chemical properties?
Bohr diagrams provide information about an atom’s stability and reactivity, while Lewis dot diagrams can be used to predict the formation and types of chemical bonds.
Are Bohr and Lewis dot diagrams still relevant in modern chemistry?
Yes, these diagrams remain essential tools for understanding atomic structure and chemical bonding, despite the development of more advanced computational methods.
