Refer to figure 6 2 the price ceiling causes quantity – Refer to Figure 6.2: The Price Ceiling Causes Quantity Supplied to Decrease delves into the captivating realm of price ceilings, exploring their profound impact on quantity supplied, market dynamics, and the intricate interplay between supply and demand. This insightful analysis unravels the complexities of price controls, shedding light on their potential consequences and the alternative policy options available to address market inefficiencies.
The concept of a price ceiling, a government-imposed maximum price for a good or service, sets the stage for this exploration. By delving into real-world examples, we uncover the ways in which price ceilings can disrupt market equilibrium, leading to shortages, black markets, and unintended negative consequences for both consumers and producers.
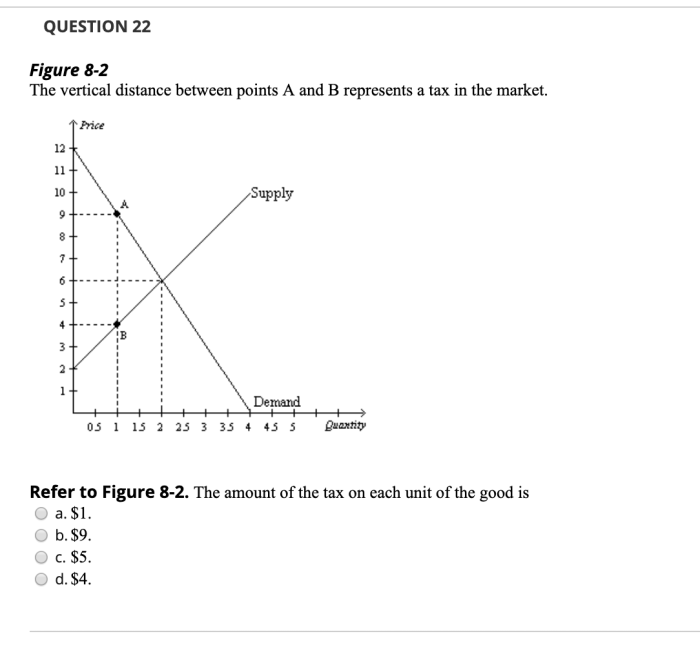
Price Ceiling and Quantity Supplied: Refer To Figure 6 2 The Price Ceiling Causes Quantity
A price ceiling is a government-imposed maximum price that can be charged for a good or service. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, it can have a significant impact on the quantity supplied.
When the price of a good or service is set below the equilibrium price, suppliers are less willing to produce and sell that good or service. This is because they can make more money by selling other goods or services that are not subject to price ceilings.
As a result, the quantity supplied of the good or service with the price ceiling will decrease.
Example
For example, if the government sets a price ceiling on gasoline below the equilibrium price, gas stations will be less willing to sell gasoline. This is because they can make more money by selling other products, such as snacks and drinks.
As a result, the quantity of gasoline supplied will decrease.
Reasons for Implementing Price Ceilings
- To protect consumers from high prices.
- To ensure that essential goods and services are available to everyone.
- To prevent price gouging.
Price Ceiling and Quantity Demanded
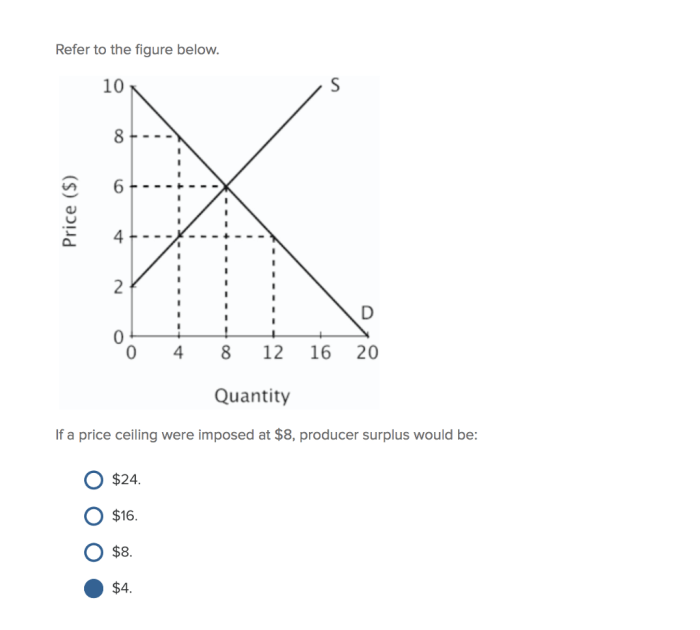
A price ceiling can also affect the quantity demanded for a good or service. When the price of a good or service is set below the equilibrium price, consumers are more likely to demand that good or service. This is because they can get it for a lower price than they would if the price were higher.
Example
For example, if the government sets a price ceiling on bread below the equilibrium price, consumers will be more likely to buy bread. This is because they can get it for a lower price than they would if the price were higher.
As a result, the quantity demanded for bread will increase.
Reasons Why a Price Ceiling Might Lead to Shortages
- The quantity supplied of the good or service decreases.
- The quantity demanded for the good or service increases.
Equilibrium Price and Quantity
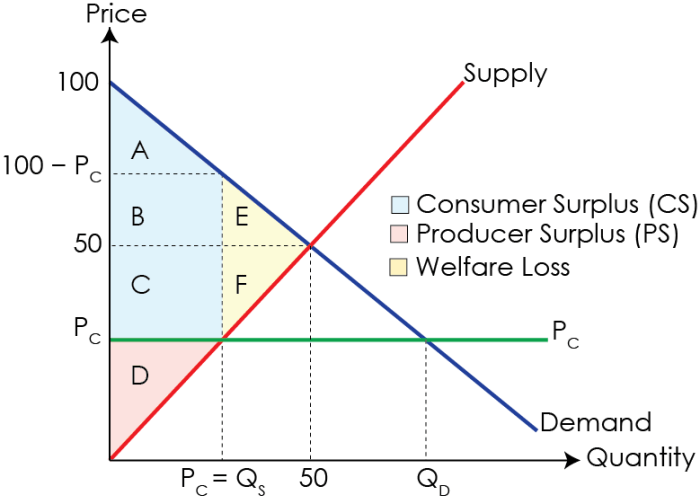
The equilibrium price is the price at which the quantity supplied of a good or service is equal to the quantity demanded. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, it can disrupt the equilibrium.
Consequences of a Price Ceiling Set Below the Equilibrium Price
- Shortages
- Black markets
- Price gouging
Market Disequilibrium and Shortages
When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, it can create market disequilibrium. This is because the quantity supplied of the good or service is less than the quantity demanded.
Example of a Price Ceiling that Leads to a Shortage, Refer to figure 6 2 the price ceiling causes quantity
For example, if the government sets a price ceiling on milk below the equilibrium price, there will be a shortage of milk. This is because the quantity of milk supplied will be less than the quantity of milk demanded.
Potential Negative Effects of Shortages on Consumers and Producers
- Consumers may have to pay higher prices for the good or service.
- Consumers may not be able to find the good or service they want.
- Producers may lose money because they are unable to sell all of their products.
Black Markets and Price Gouging
Price ceilings can lead to the emergence of black markets. A black market is an illegal market where goods and services are sold at prices above the legal price ceiling.
Example of a Price Ceiling that has Resulted in Black Market Activity
For example, during World War II, the U.S. government imposed a price ceiling on gasoline. This led to the emergence of a black market for gasoline, where gasoline was sold at prices above the legal price ceiling.
Potential Negative Consequences of Black Markets
- Consumers may have to pay higher prices for the good or service.
- Consumers may not be able to find the good or service they want.
- Black markets can lead to crime and violence.
Alternative Policy Options
There are a number of alternative policy options that can be used to address the issues caused by price ceilings. These include:
- Subsidies
- Tax breaks
- Government-owned businesses
Advantages and Disadvantages of Alternative Policy Options
| Policy Option | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Subsidies | – Can help to keep prices low for consumers.
|
– Can be expensive for the government.
|
| Tax breaks | – Can help to reduce the cost of production for businesses.
|
– Can be difficult to administer.
|
| Government-owned businesses | – Can provide essential goods and services at low prices.
|
– Can be inefficient.
|
Potential Effectiveness of Alternative Policy Options in Achieving Desired Outcomes
The effectiveness of alternative policy options in achieving desired outcomes will vary depending on the specific circumstances. However, some general observations can be made.
- Subsidies can be effective in keeping prices low for consumers, but they can also be expensive for the government.
- Tax breaks can be effective in reducing the cost of production for businesses, but they can also lead to lost revenue for the government.
- Government-owned businesses can be effective in providing essential goods and services at low prices, but they can also be inefficient.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the primary effect of a price ceiling on quantity supplied?
A price ceiling typically leads to a decrease in quantity supplied, as producers are less willing to offer goods or services at the artificially low price.
Can price ceilings ever lead to an increase in quantity supplied?
In rare cases, a price ceiling set above the equilibrium price may incentivize producers to increase supply.
What are the potential negative consequences of price ceilings?
Price ceilings can lead to shortages, black markets, reduced quality of goods or services, and unintended negative consequences for consumers and producers.